What is a computer?
A computer is an electronic device that can be used to store, analyze, and process data. When the abacus and other similar inventions happened, the person who calculates the numerical problems on them is referred to as ‘Human Computers’. Later, it was renamed ‘Computers’. The first digital computer was developed during World War II by ‘John Mauchly and ‘J. Presper Eckert at the University of Pennsylvania and named as ‘ENIAC’. The full form of this is ‘Electronic Numerical Integrator and Calculator. All the calculations that were first done by humans themselves were now done through this computer. This makes the calculations error-free and faster. The only drawback that these early computers have is that they were huge in size as they use vacuum tubes. At that time, a single computer can take up a room-size space. Due to this, they are not portable computers. This is the reason that we could find them only in workplaces or universities.
Soon after, computers have invented that work on transistors. This way the computers became small and cheap so that a common person can buy them. And this evolution continues to this day.
The computers work as a binary system that is only two variables ‘0’ and ‘1’ used for processing any task. The computer understands only the binary language. In this Century, we are surrounded by computers. There are many different types of computers that we use in our daily life such as Mobile phones, Calculators, and Televisions.
How does a computer work?
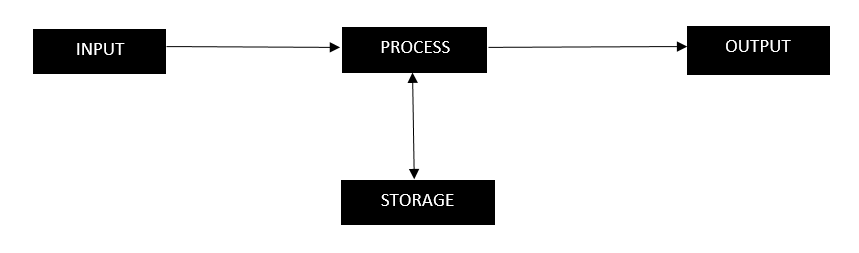
The main function that a computer performs is to allow the user to send data to the computer and process it and converts it into useful information (output) and store it in its memory.
The computers work as a binary system that is only two variables ‘0’ and ‘1’ used for processing any task. The computer understands only the binary language. In this Century, we are surrounded by computers. There are many different types of computers that we use in our daily life such as Mobile phones, Calculators, and Televisions.
Tasks a computer can perform
The computer comprises of sub-programs like input system, memory, and output system that work together to form an integrated system. A computer is a device that is used to process and analyze data and convert it into some meaningful information. A computer can also work as a calculator as it can perform basic arithmetic operations as well as advanced math problems. It can also perform logical operations. In conclusion, we can say that a computer is an electronic device that can perform all types of complex arithmetic and logical operation on its own.
Computers are also used for the representation of data through different mediums and make the whole process quicker. There are many other advantages of using a computer:
· Boosts the speed of data processing.
· Handles huge bulk of data easily.
· Evaluation of data becomes easy and quick.
· Rechecking and debugging data are easy.
· Comparative evaluation can be done through maps and graphs.
The computer provides many other benefits other than these. You can practically observe them by using a computer.
Basic parts of the computer
We are living in the 21st Century, where the computer is an essential part of our life. It doesn’t matter which field we belong to; we just need a computer in our daily routine. A computer consists of different terms, theories, and parts that a person should know to understand the computer well.
· CPU
The full form of CPU is ‘Central Processing Unit’. CPU is known as the brain of the computer. All the functions and operations are performed in this processing unit. The CPU handles, manipulates, calculates, and arranges data for output purposes.
· Hard Disk Drive
A hard disk drive is a non-volatile data storage device. Non-volatile devices are used to store data permanently for future use. In this way, all the important data that shouldn’t get removed must be saved on this hard disk. This makes the processing so much easier and quicker. Normally, a hard disk drive is fitted inside the computer.
· RAM
The full form of RAM is ‘Random Access Memory which is a temporary storage platform where we can store data while processing. RAM is a short-term memory allocation where data can be stored temporarily for processing. RAM further has two types:
1. SRAM
2. DRAM
· Software
Computer software is a program that consists of all the instructions needed for a computer to perform any task and work well. In other words, we can say that software comprises files that are used to carry out different operations on the computer.
· Hardware
All the physical parts of a computer are categorized as ‘Hardware’ of the computer. The most common examples of computer hardware are:
o Monitor
o Mouse
o Keyboard
o Motherboard
o Joystick
o Desktop
Full form of Computer (abbreviations)
The table below shows all computer full form (abbreviation) and their full forms that are being used in today’s world.
| Word | Abbreviation |
| PC | Personal Computer |
| CPU | Central Processing Unit |
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| BCD | Binary Coded Decimal |
| FM | Frequency Modulation |
| ASCII | American Standard Code for Information Interchange |
| BASIC | Beginners All-purpose Symbolic Instruction Code |
| ALGOL | Algorithmic Language |
| ALU | Arithmetic Logic Unit |
| ARPANET | Advanced Research Project Agency Network |
| BIPS | Billions of Instructions Per Second |
| EBCDIC | Extended Binary Coded Decimal Interchange Code |
| BIOS | Basic Input Output System |
| CAD | Computer Aided Design |
| FMS | File Management System |
| BPI | Bytes Per Inch |
| CAN | Campus Area Network |
| DSN | Distributed Systems Network |
| CDC | Control Data Corporation |
| EDSAC | Electronic Delay Storage Automatic Calculator |
| EDVAC | Electronic Discrete Variable Automatic Calculator |
| EPROM | Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory |
| CASE | Computer Aided Software Engineering |
| PAN | Personal Area Network |
| CAE | Computer Aided engineering |
| CD | Compact Disk |
| ROM | Read Only Memory |
| RAM | Random Access Memory |
| CL | Command Language |
| FTP | File Transfer Protocol |
| DNA | Digital Network Architecture |
| ENIAC | Electronic Numerical Integrator and Calculator |
| CD-R | CD-Recordable |
| FDM | Frequency Division Multiplexing |
| DPI | Dots Per Inch |
| FEP | Front End Processor |
| FT | Formula Translation |
| GB | Giga Bytes |
| TB | Tera Bytes |
| KB | Kilo Bytes |
| MB | Mega Bytes |
| GHZ | Giga Hertz |
| CLI | Command Line Interface |
| COBOL | Common Business Oriented Language |
| CRT | Cathode Ray Tube |
| DBMS | Data Base Management System |
| DMA | Direct Memory Access |
| WAN | Wide Area Network |
| HSS | Hierarchical Storage System |
| JPEG | Joint Photographic Experts Group |
| IDA | Infrared Data Association |
| WLL | Wireless Local Loop |
| ABC | Atanasoff Berry Computer |
| VGA | Video Graphics Array |
| USB | Universal Serial Bus |
| UPC | Universal Product Code |
| SRAM | Static RAM |
| WORM | Write Once Read Many |
| CDC | Control Data Corporation |
| CD-RW | CD Read/Write |
| DDL | Data Definition Language |
| SNA | Systems Network Architecture |
| DEC | Digital Equipment Corporation |
| DTS | Digital Theater System |
| FLOPS | Floating Point Operations Per Second |
| EPIC | Explicitly Parallel Instruction Computing |
| SIMM | Single In-line Memory Module |
| LED | Light Emitting Diode |
| MIPS | Millions of Instructions Per Second |
| MVT | Multiprogramming with Variable Tasks |
| LSI | Large Scale Integration |
| OCR | Optical Character Recognition |
| PIP | Peripheral Interchange Program |
| SDLC | Software Development Life Cycle |
| SEQUEL | Structured English Query Language |
| SQL | Structured Query Language |
| DRAM | Dynamic RAM |
| DVD | Digital Video Disk |
| GUI | Graphical User Interface |
| HSS | Hierarchical Storage System |
| HTML | Hyper Text Markup Language |
| PROM | Programmable Read-Only Memory |
| Portable Document Format | |
| OS | Operating System |
| OMR | Optical Mark Reader |
| NOS | Network Operating System |
| NIC | Network Interface Card |
| SGML | Syntax for Generalized Markup Language |
| SNOBOL | String Oriented and symbolic Language |
| UDP | User Datagram Protocol |
| VoIP | Voice over Internet Protocol |
| VCR | Video Cassette Recorder |
| WiMAX | Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access |
| MS-DOS | Microsoft Disk Operating System |
| MNP | Micro-com Network Protocol |
| MBR | Memory Buffer Register |
| HTTP | Hyper Text Transport Protocol |
| IBM | International Business Machine |
| IC | Integrated Circuit |
| XML | Extensible Markup Language |
| XHTML | Extensible Hyper Text Markup Language |
| WWW | World Wide Web |
| LAN | Local Area Network |
| WLAN | Wireless Local Area Network |
| WAP | Wireless Application Protocol |
| MAR | Memory Address Register |
| MAN | Metropolitan Area Network |
| LCD | Liquid Crystal Display |
| KHz | Kilo Hertz |
| JRE | Java Runtime Engine |
| JSP | Java Server Pages |
| ISP | Internet Service Provider |
| ISDN | Integrated Services Digital Network |
| IP | Internet Protocol |
| IDN | Integrated Digital Networks |
| ACM | Association for Computing Machinery |
